Autodesk Inventor vs. Advance Steel: A Detailed Comparison
Autodesk Inventor vs. Advance Steel: A Detailed Comparison
Choosing the right design software can make or break a project, especially when you’re dealing with complex structures or intricate mechanical systems. If you’re in the engineering or construction world, you’ve likely heard the debate about Autodesk Inventor vs Advance Steel—two industry-leading tools, each designed to tackle different challenges.
In this comprehensive comparison, we’ll explore the strengths of both software packages, breaking down their features and applications so you can make an informed decision. Whether you’re building next-generation machinery or detailing a steel structure for a high-rise building, understanding these tools’ capabilities will ensure you’re leveraging the best technology for your needs.
So, if you’re ready to elevate your engineering or construction projects, let’s dive into the intricate details that set Autodesk Inventor vs Advance Steel apart. Buckle up—this deep dive will give you the insights you need to choose wisely and maximise efficiency, accuracy, and innovation in your next project.
Overview of Autodesk Inventor
Autodesk Inventor is a comprehensive 3D CAD software primarily used for mechanical design. It supports a wide range of applications, from product design to manufacturing, enabling engineers to create highly detailed models, prototypes, and documentation.
Key Features of Autodesk Inventor for Steel Design and Fabrication
- Parametric Modelling: Inventor’s parametric design capabilities allow engineers to define and manipulate relationships between elements, facilitating easy updates and modifications throughout the design process.
- Frame Generator: This tool simplifies the creation of structural frames. Users can quickly generate accurate frame designs using pre-configured components, which is particularly useful in fabricating steel structures. Frame Generator: This tool simplifies the creation of structural frames. Users can quickly generate accurate frame designs using pre-configured components, which is particularly useful in fabricating steel structures. However, Inventor’s Frame Generator lacks the advanced editing and automation functions that Advance Steel offers for creating connections, cuts, trims, notches, and more.
- Large Content Library: Inventor includes an extensive library of components such as fasteners, structural shapes, and other mechanical parts, enabling efficient design workflows without the need to create standard components from scratch.
- Integrated Simulation: Engineers can run simulations directly within Inventor to assess stress, motion, and deflection. This feature helps optimise designs before manufacturing, reducing the need for physical prototypes.
- Sheet Metal Design: Both Inventor and Advanced Steel have sheet metal tools. In Inventor the module is called Sheet Metal and in Advance Steel, it’s referred to as Folded Plate.
- Automated Documentation: Using the integration with the iLogic design automation programming environment, you can automate manufacturing drawings, complete with dimensions, annotations, and BOMs (Bills of Materials), ensuring consistency and reducing manual errors.
Ideal Use Cases for Autodesk Inventor
- Architectural Fabrication: Inventor has the flexible 3D modelling tools to design fabricated products that are aesthetic, ergonoic or organic in design, where as Advance Steel is better suited for straight lines and industrial projects.
- Mechanical Engineering: Inventor is well-suited for designing mechanical systems and components that require precision and the ability to simulate real-world performance.
- Product Development: Its comprehensive toolset allows for detailed product design, from concept to final prototype.
- Structural Fabrication: Although primarily a mechanical tool, Inventor can handle structural steel design, making it versatile for mixed mechanical and structural projects.
Overview of Advance Steel
Advance Steel is a specialised software focused on structural steel detailing. It integrates seamlessly with BIM (Building Information Modelling) workflows, providing tools for automating the creation of detailed fabrication drawings, models, and documentation required for steel construction.
Key Features of Advance Steel
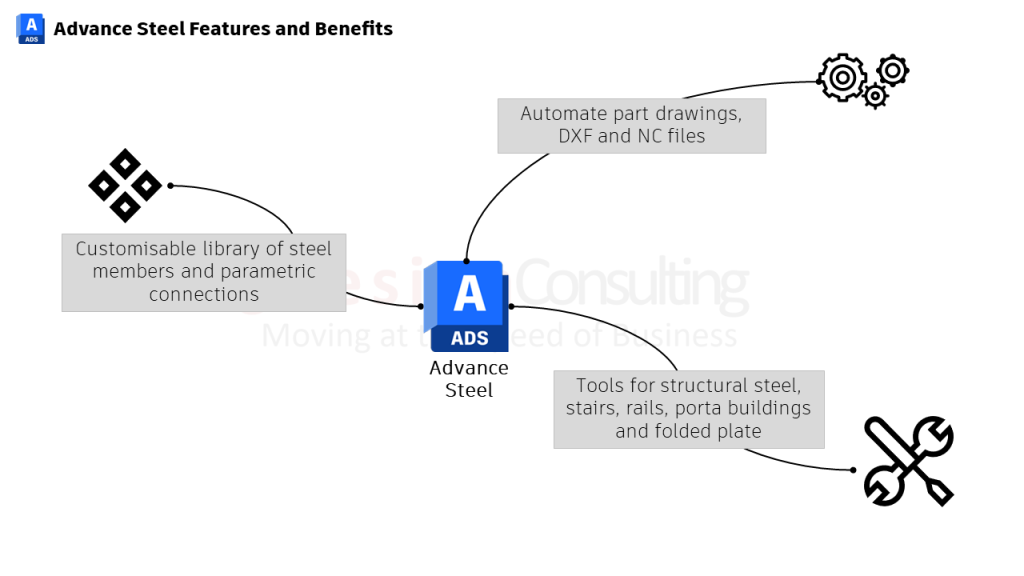
- Specialised Steel Detailing Tools: Advance Steel is purpose-built for structural detailing, offering tools that cater specifically to the needs of steel fabricators and structural engineers. These tools include advanced steel editing and automation functions for making cuts, trims, and notches.
- Automatic Fabrication Drawings: The software can automatically generate comprehensive fabrication drawings, reducing the time from design to production and ensuring all structural elements are accurately detailed.
- Connection Libraries: Advance Steel includes a vast library of pre-configured steel connections, making it easier to apply standardised joints in structural designs. Users can also create custom connections to meet specific project requirements. Inventor, on the other hand, lacks this advanced parametric connection library.
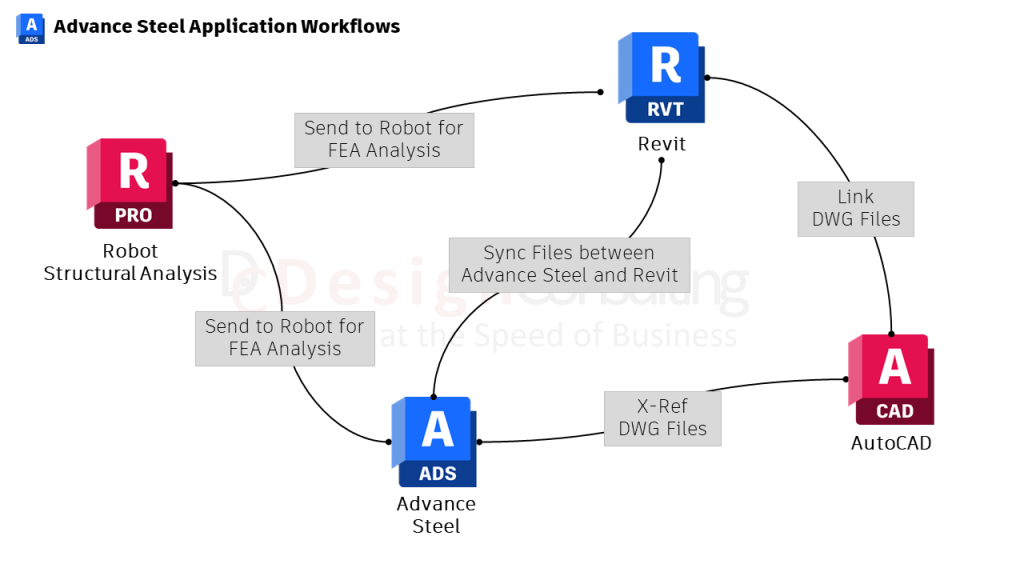
- BIM integration: Advance Steel syncs seamlessly with Revit, while Inventor also offers BIM integration, including the ability to export to Revit as RVT or RFA files.
- Efficient Material Management: The software automates the generation of BOMs, cut lists, and material takeoffs, streamlining the process of inventory management and cost estimation in construction projects.
- Advanced Documentation and Revision Control: Advance Steel’s documentation features are tightly integrated with the model, ensuring that changes to the design automatically update all associated drawings and documentation.
Ideal Use Cases for Advance Steel
- Structural Engineering: Advance Steel is ideal for engineers who focus on the design, detailing, and documentation of steel structures.
- Steel Fabrication: The software’s automation capabilities make it invaluable for fabricators who require precise and efficient production workflows.
- Construction Projects: Its BIM integration and detailed documentation support complex construction projects involving structural steel.
Feature Comparison of Overlapping Tools
Both Autodesk Inventor and Advance Steel offer tools that overlap in the realm of metal design, particularly in frame generation and sheet metal design. Here’s a detailed comparison of these features:
Frame Generation and Steel Editing
- Autodesk Inventor Frame Generator:
- Allows users to create structural frames quickly using predefined components.
- Supports basic bolted connections and weldments.
- Limitations: Lacks connection library and advanced editing capabilities and automation for cuts, trims, and notches compared to Advance Steel.
- Advance Steel Steel Editing:
- Offers advanced tools for creating and modifying steel structures, including automated functions for cuts, trims, and notches.
- Includes a parametric connection library that automatically adjusts connection sizes based on member dimensions.
- Strengths: Provides comprehensive tools for stairs, rails, and portal buildings, which Inventor does not offer.
Sheet Metal Design
- Inventor Sheet Metal Design:
- Provides tools for creating and manipulating sheet metal parts, including folding and cutting.
- Applications: Ideal for industries requiring detailed sheet metal fabrication.
Automation and Documentation
- Inventor Automation:
- Has a 2D/3D automation for drawing environments and exporting DXF files.
- Complexity: 3D automation and basic 2D automation are relatively easy, fully automating part drawings can be complex
- Advance Steel Automation:
- Provides robust automation for part drawings, DXF files for laser/plasma cutters, and NC1 G-code for beamline machines.
- Efficiency: Streamlines the documentation process, making it faster and more reliable.
Autodesk Inventor vs Advance Steel: Key Differences
| Feature | Autodesk Inventor | Advance Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | 3D Mechanical Design | Structural Steel Detailing |
| Primary Application | Product Development, Mechanical Systems, Fabrication | Steel Structures, Construction Projects |
| Industry | Product Design, Industrial Machinery | Construction, Structural Engineering |
| Modelling Capabilities | Parametric Mechanical Components | Detailed Steel Structures and Connections |
| Simulation Tools | Integrated for Mechanical Parts | None. Need to export to Robot or other FEA packages |
| BIM Support | No bidirectional Sync tool with Revit but offers many sync workflows and import/export capabilities | Syncs with Revit and Robot structural analysis |
| Documentation | Automated Manufacturing Drawings | Automated Fabrication Drawings |
| Steel Editing Tools | Frame Generator | Advanced Steel Editing and Automation |
| Connection Libraries | Limited | Vast Parametric Connection Library |
| Specialised Tools | Sheet Metal Design | Folded Plates, Stairs, Rails, Portal Buildings |
| Drawing Automation | Complex to set up | Automated through a Dedicated Tool |
| Fabrication Automation | DXF Export | DXF, NC1(G-Code Export) |
Autodesk Inventor vs Advance Steel: Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
When to Use Autodesk Inventor
Inventor is the optimal choice for projects that require detailed mechanical design, particularly in industries like automotive, aerospace, and product development. It provides the necessary tools for creating, testing, and refining mechanical parts and assemblies, making it ideal for engineers who need to model complex components and simulate their behaviour under various conditions. In addition to its robust design capabilities, Inventor excels in modeling complex shapes with curvature, making it especially useful for designs that require intricate and organic geometries. Its frame generator and sheet metal design tools can also be beneficial for certain structural steel projects.
When to Use Advance Steel
Advance Steel is the go-to software for professionals in structural engineering and steel fabrication. Its specialised tools and BIM integration make it essential for efficiently detailing and documenting steel structures in construction projects. It is particularly beneficial for fabricators who need to automate drawing production and ensure compliance with industry standards. Advance Steel’s advanced steel editing tools, parametric connection library, and specialised features like folded plate, stairs, rails, and portal buildings make it the superior choice for complex structural steel projects. However, while Advance Steel excels in structural steel detailing, it may not be the best option for projects involving curved shapes.
This means that for architectural applications requiring curvature, Inventor is the better tool, whereas, for industrial applications, Advance Steel proves to be the superior choice.
Autodesk Inventor and Advance Steel integration
While both tools are better at certain tasks, you can still integrate both tools and combine their tool sets to create more detailed designs. Here’s how it works.
Steps to Convert IFC Components into Advance Steel Members:
- Import the IFC File:
Use the Import function in Advance Steel to bring the IFC file into your project.
Go to Home > Import > IFC and select the IFC file.
The IFC components will be imported into Advance Steel as 3D solids, and they won’t initially be recognized as standard Advance Steel members like beams or columns. - Inspect the Imported Geometry:
After importing the IFC file, inspect the components to understand the structural elements (e.g., beams, columns, plates) that need to be converted into Advance Steel members.
Use the Object Inspector or Properties panel to check the dimensions and placement of each component. - Convert Geometry to Advance Steel Objects:
To convert IFC objects (such as solids) into parametric Advance Steel members, you can use the “Convert to Advance Steel Object” feature:
- Import the IFC File:
- Beams and Columns: For linear objects that represent beams or columns, you can use the Beam Conversion Tool to convert them into standard Advance Steel beams.
Use the “Advance Steel Beams” command to recreate the IFC solid as a native Advance Steel beam. This will allow you to assign profiles and cross-sections, as well as work with connections and detailing tools. - Plates: If the IFC model contains plates or sheet elements, you can convert these into Advance Steel plates using the Plate Tool. This lets you add cuts, bolts, and welding details.
- Beams and Columns: For linear objects that represent beams or columns, you can use the Beam Conversion Tool to convert them into standard Advance Steel beams.
- Assign Structural Properties:
After converting the geometry to Advance Steel members, assign the appropriate material, section type, and structural properties to each member.
You can also apply Advance Steel’s intelligent connections (e.g., bolt groups, welds, stiffeners) to the converted members. - Refine the Model:
Depending on the complexity of the IFC import, some components might require further manual adjustments or reconstruction to align with Advance Steel’s parametric modeling system.
For example, custom connection types from IFC may need to be rebuilt using Advance Steel’s native tools for connections. - Save the Converted Model:
Once the conversion is complete, save the model as an Advance Steel project. You can now take advantage of Advance Steel’s automated detailing, fabrication drawings, and BOM generation features for your newly converted members.
- Assign Structural Properties:
Unlock Your Design Potential—Choose the Right Tool for Success
Autodesk Inventor vs Advance Steel is a debate that is likely to continue, given how powerful both tools are. Inventor excels in mechanical design and product development, offering robust simulation and modelling capabilities. Advance Steel, on the other hand, is unparalleled in its ability to streamline structural steel detailing and integrate seamlessly with BIM workflows.
So, based on your requirements and the demands of the projects you’re working on, make sure to choose the right product that will help you deliver great results. If your focus is on mechanical design and product development, Inventor is the clear choice. But if you’re working on complex structural steel projects that require advanced detailing, automation, and BIM integration, Advance Steel is the superior option.
Contact Us
Contact us to find out how we can help your business. Fill out the form below, by live chat, phone or email.
P: 1800 490 514 | E: [email protected]